Vocabulary
AUCTIONS AND BUY NOW CARS
AUTO AUCTION: marketplace for new and used vehicles where buyers and sellers meet.
There are over 130 car auctions throughout Japan. Sellers bring their cars to the auction, and
buyers place bids on them. The highest bidder gets the right to purchase the vehicle. In current
days, due to the large amount of vehicles going on auction everyday, most of the auctions are placed
online in real time.
INSPECTION SHEET: document attached to each vehicle that has been issued by the auction house inspector, after checking the vehicles carefully.
BID: amount of money that the bidder is willing to pay for a particular vehicle.
INSPECTION SHEET: document attached to each vehicle that has been issued by the auction house inspector, after checking the vehicles carefully.
BID: amount of money that the bidder is willing to pay for a particular vehicle.
LOT: number that the auction house gives to each car. This is like an ID number and
its
function is the easy search of a particular vehicle.
RESERVED PRICE: minimum amount of money that the seller of a vehicle has set. If bids reach that amount or higher, the car becomes sold to the highest bidder. If the highest bid is inferior to the reserved price, the car becomes unsold.
BUY NOW CARS: vehicles that are sold at channels other than auctions. In these cars, price is fixed and there is more information and pictures available. In some cases Unet Co., Ltd. can conduct an inspection on the car.
RESERVED PRICE: minimum amount of money that the seller of a vehicle has set. If bids reach that amount or higher, the car becomes sold to the highest bidder. If the highest bid is inferior to the reserved price, the car becomes unsold.
BUY NOW CARS: vehicles that are sold at channels other than auctions. In these cars, price is fixed and there is more information and pictures available. In some cases Unet Co., Ltd. can conduct an inspection on the car.
LOGISTICS WITHIN JAPAN
INLAND TRANSPORTATION: transportation from auction house or location where the car
is,
to the port of departure.
CUSTOMS CLEARANCE: process where the cars get cleared and ready to be exported.
CUSTOMS CLEARANCE: process where the cars get cleared and ready to be exported.
RADIATION SURVEY: Due to the Fukushima incident bank in 2011, all the vehicles
exported
must comply with rules in order to protect customers overseas. No cars with radiation can be
exported
from Japan.
VANNING: container stuffing.
Terminal Handling Charge (THC): related to container shipments, this refers to the crane that is used to load the container onto the ships.
VANNING: container stuffing.
Terminal Handling Charge (THC): related to container shipments, this refers to the crane that is used to load the container onto the ships.
DOCUMENTS
BILL OF LADING (B/L): A bill of lading is like a ticket for cargo. For receipt of
the
shipment, the original must be submitted to the carrier’s destination agent, unless the bill of
lading
has been surrendered.
EXPORT CERTIFICATE: Document that is issued after deregistration in Japan is accomplished. This document states all the vehicle information and is required for the customs clearance prior to shipment and upon arrival to the port of destination.
EXPORT CERTIFICATE: Document that is issued after deregistration in Japan is accomplished. This document states all the vehicle information and is required for the customs clearance prior to shipment and upon arrival to the port of destination.
SURRENDER (of Bill of Lading): after the merchandise departs from Japan, the Bill
of
Lading is issued by the shipping company. Bill of Lading is issued in paper. By surrendering the
Bill of
Lading, the paper documents get surrendered and an electronic Bill of Lading in PDF is issued on its
behalf.
Letter of Guarantee (L/G): in some cases, there are changes to be made after a Bill of Lading is issued. In order to do so, it's necessary to submit a Letter of Guarantee to the shipping line to amend the Bill of Lading.
Letter of Guarantee (L/G): in some cases, there are changes to be made after a Bill of Lading is issued. In order to do so, it's necessary to submit a Letter of Guarantee to the shipping line to amend the Bill of Lading.
TRANSACTION INCOTERMS
INCOTERM: The Incoterms or International Commercial Terms are a series of
predefined
commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) relating to international
commercial law
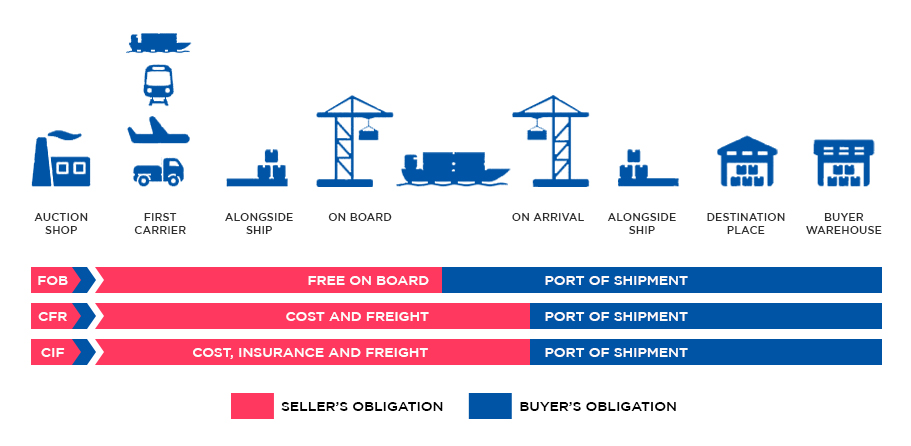

FOB – Free on Board (named port of shipment)
Under FOB terms the seller bears all costs and risks up to the point the goods are loaded on board
the
vessel. The seller's responsibility does not end at that point unless the goods are "appropriated to
the
contract" that is, they are "clearly set aside or otherwise identified as the contract goods.
Therefore,
FOB contract requires a seller to deliver goods on board a vessel that is to be designated by the
buyer
in a manner customary at the particular port.
In this case, the seller must also arrange for export clearance. On the other hand, the buyer pays
cost
of marine freight transportation, bill of lading fees, insurance, unloading and transportation cost
from
the arrival port to destination
CIF – Cost, Insurance & Freight (named port of destination)
This term is broadly similar to the above CFR term, with the exception that the seller is required
to
obtain insurance for the goods while in transit to the named port of destination.The seller must
also
turn over documents necessary, to obtain the goods from the carrier or to assert claim against an
insurer to the buyer.
The documents include (as a minimum) the invoice, the insurance policy, and the
bill of lading. These three documents represent the cost, insurance, and freight of CIF. The
seller's
obligation ends when the documents are handed over to the buyer. Then, the buyer has to pay at the
agreed price.
C&F / CFR – Cost and Freight (named port of destination)
The seller pays for the carriage of the goods up to the named port of destination. Risk transfers to
the
buyer when the goods have been loaded on board the ship in the country of Export. The Shipper is
responsible for origin costs including export clearance and freight costs for carriage to the named
port.
The shipper is not responsible for delivery to the final destination from the port (generally the
buyer's facilities), or for buying insurance. If the buyer does require the seller to obtain
insurance,
the Incoterm CIF should be considered
SHIPPING & ROLES
SHIPPING: refers to the shipping by RORO or Container.
ROLL ON ROLL OFF SHIPMENT (RO-RO): ships are ferries designed to carry wheeled cargo, such as cars, trucks, semi-trailer trucks, trailers, and railroad cars, that are driven on and off the ship on their own wheels or using a platform vehicle, such as a self-propelled modular transporter.
CONTAINER SHIPMENT: cargo ships that carry all of their load in truck-size intermodal containers, in a technique called containerization. They are a common means of commercial intermodal freight transport and now carry most seagoing non-bulk cargo.
Container ship capacity is measured in twenty-foot equivalent units (TEU). Typical loads are a mix of 20-foot and 40-foot (2-TEU) ISO-standard containers, with the latter predominant.
ROLL ON ROLL OFF SHIPMENT (RO-RO): ships are ferries designed to carry wheeled cargo, such as cars, trucks, semi-trailer trucks, trailers, and railroad cars, that are driven on and off the ship on their own wheels or using a platform vehicle, such as a self-propelled modular transporter.
CONTAINER SHIPMENT: cargo ships that carry all of their load in truck-size intermodal containers, in a technique called containerization. They are a common means of commercial intermodal freight transport and now carry most seagoing non-bulk cargo.
Container ship capacity is measured in twenty-foot equivalent units (TEU). Typical loads are a mix of 20-foot and 40-foot (2-TEU) ISO-standard containers, with the latter predominant.
INNER CARGO: items (parts, accessories or other goods) placed inside the vehicles
in
RORO shipments. Most of the shipping lines do not accept inner cargo.
SHIPPER: A shipper is a person or a company responsible for organising and transporting goods from one point to another.
CONSIGNEE: A party (usually a buyer) named by the consignee (usually a seller) in transportation documents as the party to whose order a consignment will be delivered at the port of destination. The consignee is considered to be the owner of the consignment for the purpose of filing the customs declaration, and for paying duties and taxes NOTIFY PARTY: is merely someone that needs to be notified about the arrival of the cargo covered in the bill of lading.
SHIPPER: A shipper is a person or a company responsible for organising and transporting goods from one point to another.
CONSIGNEE: A party (usually a buyer) named by the consignee (usually a seller) in transportation documents as the party to whose order a consignment will be delivered at the port of destination. The consignee is considered to be the owner of the consignment for the purpose of filing the customs declaration, and for paying duties and taxes NOTIFY PARTY: is merely someone that needs to be notified about the arrival of the cargo covered in the bill of lading.
PAYMENTS
TELEGRAFIC TRANSFER (T/T): A telegraphic transfer (TT) is an electronic method of
transferring funds utilized primarily for overseas wire transactions.
SECURITY DEPOSIT: refers to a predetermined amount of money that the customer will deposit to enable the purchase of a vehicle both at the auctions or at local dealerships. No vehicle can be purchased without this sum being transferred to UNET Co.,Ltd.
SECURITY DEPOSIT: refers to a predetermined amount of money that the customer will deposit to enable the purchase of a vehicle both at the auctions or at local dealerships. No vehicle can be purchased without this sum being transferred to UNET Co.,Ltd.
BANK FEES SHA: means that the buyer only pays the bank's outgoing transfer charge.
The
seller receives the payment minus the correspondent (intermediary) bank charges. In Unet Co., Ltd.
we do
not accept this payment method.
BANK FEES OUR: this instruction means that the buyer will pay all transfer charges. The seller will receive your payment in full.This is the only accepted payment method accepted by Unet Co.,Ltd.
BANK FEES OUR: this instruction means that the buyer will pay all transfer charges. The seller will receive your payment in full.This is the only accepted payment method accepted by Unet Co.,Ltd.
VEHICLES
MANUFACTURE DATE: Date where the car was produced.
VEHICLE FIRST REGISTRATION: date when the car was first registered at the transportation bureau in Japan. Note that this date will be always after the MANUFACTURE DATE. In some cases, when the cars have been imported into Japan, the difference between MANUFACTURE DATE and FIRST REGISTRATION can be years.
VEHICLE FIRST REGISTRATION: date when the car was first registered at the transportation bureau in Japan. Note that this date will be always after the MANUFACTURE DATE. In some cases, when the cars have been imported into Japan, the difference between MANUFACTURE DATE and FIRST REGISTRATION can be years.
SHAKEN: compulsory technical inspection for all the vehicles using the japanese
roads must comply.
NUMBER PLATES: term used in Japan to refer to License Plates
NUMBER PLATES: term used in Japan to refer to License Plates
